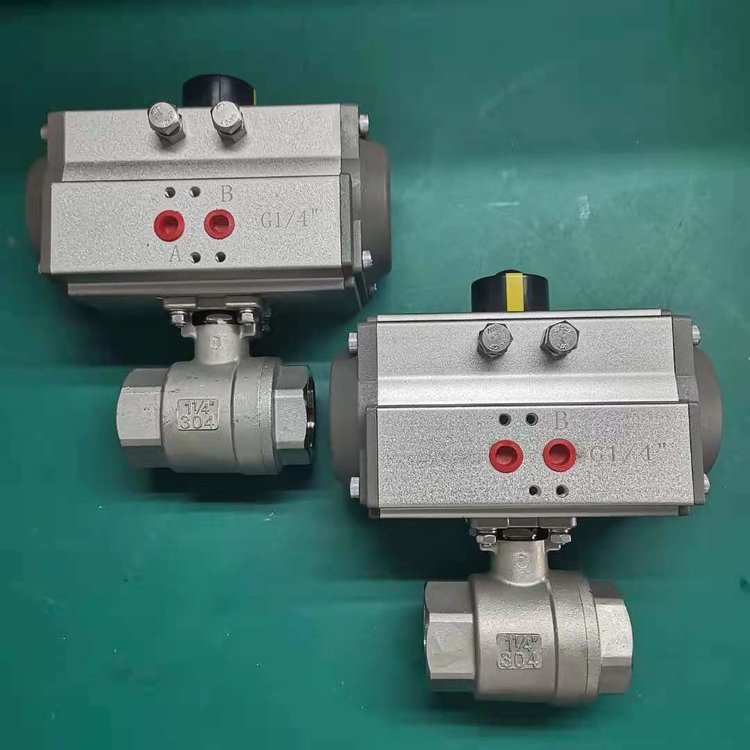
Pneumatic internal thread two-piece ball valve, Q611F
气动内螺纹二片式球阀Q611FOverviewThe pneumatic internal thread (butt-weld) ball valve cons...
气动内螺纹二片式球阀Q611FOverviewThe pneumatic internal thread (butt-weld) ball valve cons...
气动内螺纹二片式球阀Q611F

Overview
The pneumatic internal thread (butt-weld) ball valve consists of a double (single)-acting pneumatic piston actuator and an internal thread (butt-weld) ball valve.
The valve body can be classified into one-piece, two-piece, or three-piece structures. The valve seat adopts an elastic sealing structure, ensuring reliable sealing and smooth operation.
The valve stem features a bottom-mounted inverted sealing design, preventing it from being impacted in case of abnormal valve cavity pressure.
The pneumatic piston actuator uses low-friction material for the bearing sleeve, and the cylinder's inner and outer surfaces undergo hard anodizing for corrosion resistance,
significantly extending its service life. This product offers stable performance and is widely used in industrial sectors such as petrochemicals, metallurgy, power generation, light industry, and pharmaceuticals.
Working Principle
When the pneumatic actuator is connected to the circuit and the system's air supply, air enters cylinder A (or cylinder B) through pipeline A or B, driving the piston to move in one direction.
This movement rotates the shaft and ball core by 90°.
□ The top of the pneumatic actuator is equipped with a visual position indicator. When the green marker points to "OPEN," it indicates the valve is open.
□ When the signal light on the position transmitter shows green, the valve is in the open position; when red, it is closed.
□ The positioner can regulate the flow rate in the valve pipeline.
气动执行器主要技术参数
| 气动执行器 | 型号 | QW-TZ精小型系列、AT单作用系列 |
| 控制形式 | 双作用/单作用 | |
| 作用形式 | 切断/调节 | |
| 气源压力 | 0.4 ~ 0.8 MPa | |
| 最大回转角度 | 90°~92° | |
| 回信器 | AC220V AC110V DC24V | |
| 控制信号 | 电信号:0~0Ma 4 ~20Ma 气信号:0.02 ~0.1 MPa | |
| 控制气源 | 洁净、干燥压缩空气 | |
| 工作温度 | -20℃ ~ +90℃ |
阀体主要零件材料
| 零件名称 | 阀体 | 球芯 | 阀座 | 阀杆 | 填料 |
| Q611F-16Q611F-25 | 304 | 0Cr18Ni9 | 增强聚四氟乙烯 | 0Cr18Ni9 | 增强聚四氟乙烯 |
| 316 | 0Cr17Ni12Mo2 | 增强聚四氟乙烯 | 0Cr17Ni12Mo2 | 增强聚四氟乙烯 |
主要性能规范
| 型 号 | 公称压力PN(MPa) | 试验压力Ps(MPa) | 工作温度(℃) | 适用介质 | |
| 壳体 | 密封 | ||||
| Q611F-16P(R) | 1.6 | 2.4 | 1.76 | -20~150 | 水、蒸汽、油品、酸类 |
| Q611F-25P(R) | 2.5 | 3.75 | 2.75 | ||
| Q611F-40P(R) | 4.0 | 6.0 | 4.4 | ||
气动执行器主要部件材料
| 零件名称 | 缸体 | 端盖 | 活塞 | 轴 | O型圈 | 螺栓 |
| QW-TZAT | 铝合金型材硬质阳极氧化 | 压铸铝合金环氧树脂喷涂 | 压铸铝 | 钢镀镍磷合金 | NBR | SUS304 |

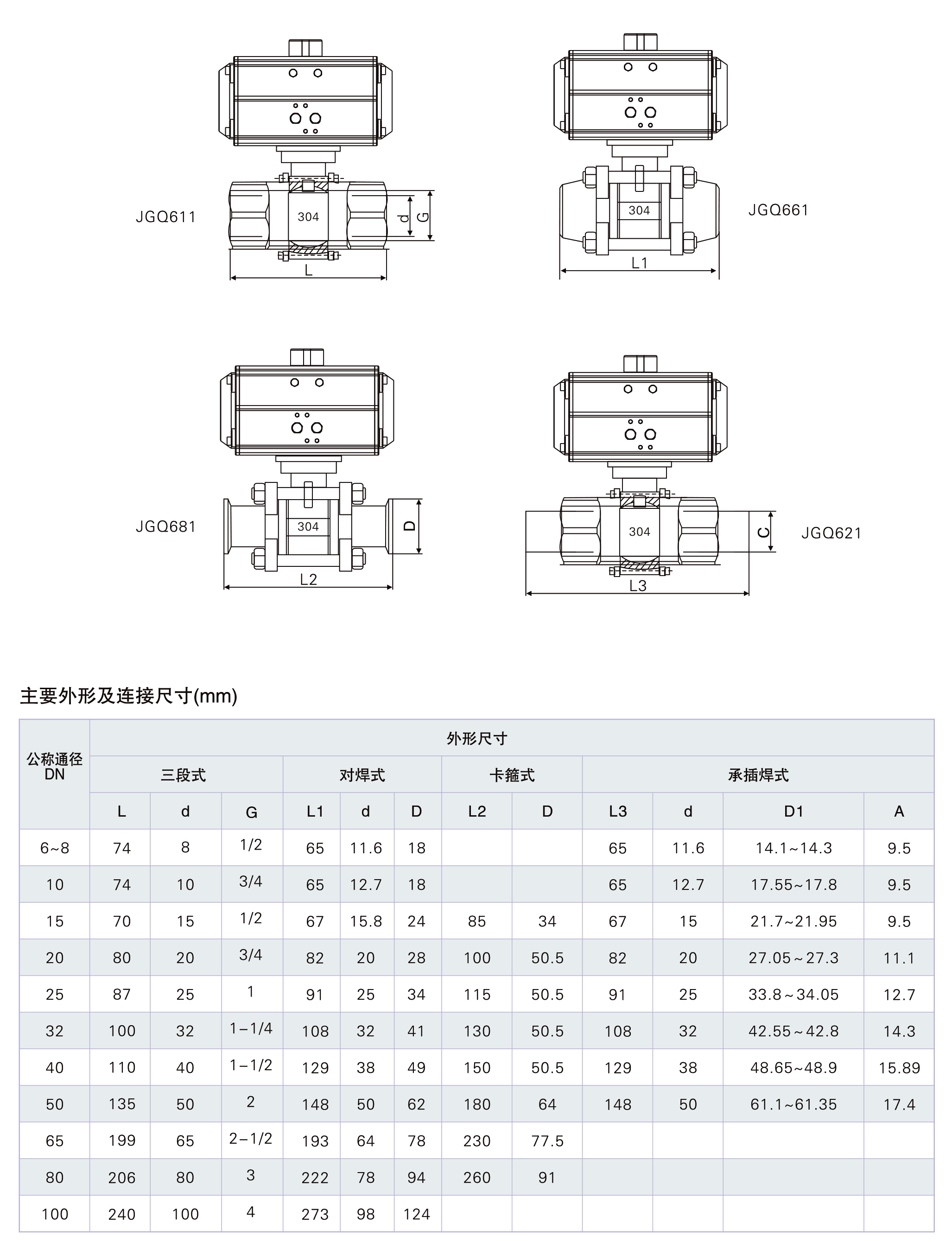
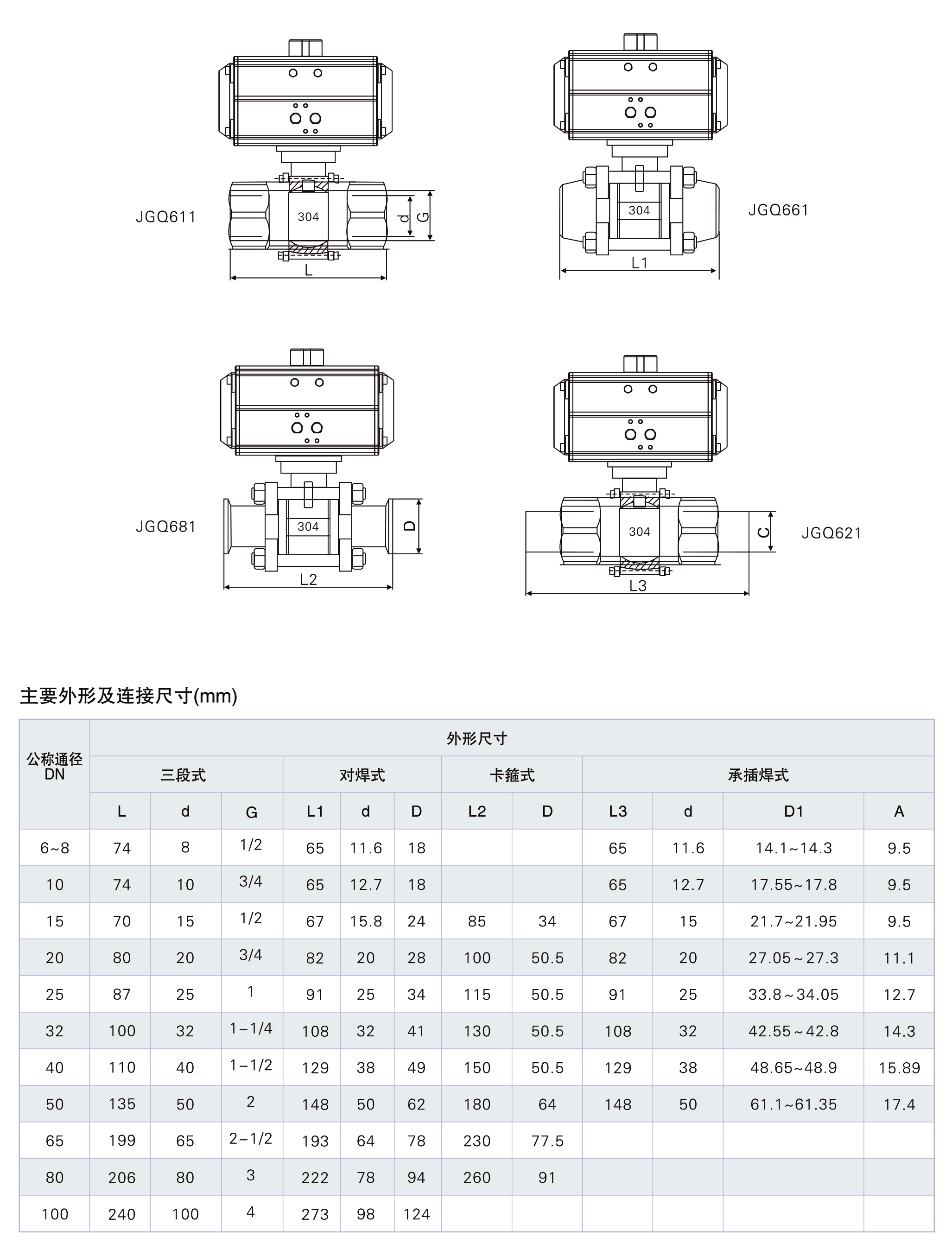
主要外形尺寸
| 公称通径 | 尺 寸 | 气动执行器 | |||||
| G | A | H | L | d | D | ||
| 10 | 3/8 | 131 | 142 | 65 | 12.7 | 18 | AT1 |
| 15 | 1/2 | 131 | 148 | 67 | 15 | 24 | AT1 |
| 20 | 3/4 | 131 | 167 | 82 | 20 | 28 | AT1 |
| 25 | 1 | 131 | 175 | 91 | 25 | 34 | AT1 |
| 32 | 11/4 | 185 | 210 | 108 | 32 | 41 | AT2 |
| 40 | 11/2 | 185 | 238 | 129 | 38 | 49 | AT2 |
| 50 | 2 | 185 | 245 | 148 | 50 | 62 | AT2 |
DN65 21/4
DN80 21/2
DN100 3"
订货须知:
一、①气动三片式球阀产品名称与型号
②气动三片式球阀口径
③气动三片式球阀是否带附件以便我们的为您正确选型。
二、若已经由设计单位选定的气动三片式球阀型号,请按气动三片式球阀型号直接向我司销售部订购。
附件的选项
根据不同控制和要求可选择下列附件:
切断型附件:单电控电磁阀、双电控电磁阀、限位开关回讯器。
调节型附件:电气定位器、气动定位器、电气转换器。
气源处理附件:空气过滤减压阀、气源处理三联件。
手动机构:手操机构
Common Faults and Solutions for Pneumatic Two-Piece Ball Valves
Common faults in pneumatic two-piece ball valves mainly include valve leakage, actuator failure, and sluggish valve operation. Below are some typical faults and their solutions:
1. Internal Valve Leakage
Symptom: Medium continues to flow downstream when the valve is closed.
Possible Causes:
Wear or damage to the sealing surfaces of the ball and seat, caused by prolonged use, medium erosion, or particle abrasion.
Foreign particles or debris trapped between sealing surfaces, affecting sealing performance.
Improper valve installation, leading to deformation and poor sealing contact.
Solutions:
Repair or replace the worn/damaged ball and seat. Minor wear can be fixed by lapping the sealing surfaces; severe damage requires replacement.
Disassemble the valve, clean any debris between sealing surfaces, and check if filters are functioning properly to prevent recontamination.
Recheck the valve installation to ensure proper alignment and no pipeline stress on the valve. Reinstall if necessary.
2. External Valve Leakage
Symptom: Medium leaks from valve connections, stem, or other external parts.
Possible Causes:
Gasket aging, damage, or improper installation at valve connections.
Wear or aging of stem seals (e.g., packing material degradation).
Casting defects (e.g., pinholes, cracks) in the valve body.
Solutions:
Replace damaged gaskets and ensure proper installation with even tightening force.
Replace stem seals (e.g., packing). Select suitable materials and install correctly for a tight seal.
Repair minor defects by welding; replace the valve body if cracks are severe.
3. Actuator Malfunction
Symptom: Valve fails to open/close, operates slowly, or lacks force.
Possible Causes:
Air supply issues (low pressure, clogged/leaking lines).
Actuator failure (piston seal damage, cylinder wear, or broken springs).
Solenoid valve failure (burnt coil, stuck spool, or seal leakage).
Solutions:
Check the air supply system—ensure proper pressure, clean lines of debris/moisture, and fix leaks.
Inspect the actuator—replace damaged piston seals, repair/replace worn cylinders, and replace faulty springs.
Test the solenoid valve—replace burnt coils, clean the spool, and repair/replace defective units.
4. Sluggish Valve Operation
Symptom: Valve sticks or hesitates during opening/closing.
Possible Causes:
Debris lodged between the ball and seat.
Excessive friction in the stem packing (over-tightened or aged).
Worn, loose, or poorly lubricated actuator transmission parts.
Solutions:
Disassemble and clean the valve interior to remove obstructions.
Adjust packing tightness or replace aged packing; apply lubricant if needed.
Inspect transmission components (gears, linkages)—replace worn parts, tighten connections, and lubricate regularly.
5. Incomplete Valve Closure
Symptom: Medium still flows after the valve is closed.
Possible Causes:
Scratches or pits on sealing surfaces.
Insufficient closing torque (undersized actuator or low air pressure).
Abnormal medium pressure exceeding the valve’s sealing capacity.
Solutions:
Lap minor sealing surface defects; replace the ball/seat if severely damaged.
Verify actuator sizing and air pressure—upgrade the actuator or adjust pressure if needed.
Stabilize medium pressure (e.g., install a pressure regulator).
Note: Regular maintenance and correct operation can significantly reduce these faults. Always follow manufacturer guidelines for installation and servicing.

Learn about the latest developments and updated designs of our products.
Submit an inquiry